Transcation의 속성
| 속성 | 설명 |
| propagation | Tx의 경계(Boundary)를 설정하는 방법을 저장 |
| isolation | Tx의 isolate level을 지정, DEFAUL, READ_UMCOMMITTED, READ_COMMITTED, REPEATABLE_READ, SERIALIZABLE Default의 경우 DB설정을 따른다(Default = REPEATABLE_READ) |
| readOnly | Tx이 데이터를 읽기만 하는경우, true로 지정하면 성능이 향상 |
| rollbackFor | 지정된 예외가 발생하면, Tx를 rollback // RuntimeException과 Error는 자동 rollback |
| noRollbackFor | 지정된 예외가 발생해도, Tx을 Rollback하지 않음 |
| timeout | 지정된 시간(초) 내에 Tx이 종료되지 않으면, Tx를 강제종료 |
propagation 속성의 값
| 값 | 설명 |
| REQUIRED | Tx이 진행중이면 참여하고, 없으면 새로운 Tx시작(디폴트) |
| REQUIREDS_NEW | Tx이 진행 중이건 아니건, 새로운 Tx 시작 ( Tx안에 다른 Tx 생성) |
| NESTED | Tx이 진행 중이면, Tx의 내부 Tx로 실행 ( Tx안에 subTx같은 Tx생성) - save point |
| MANDATORY | 반드시 진행 중인 Tx 내에서만 실행가능, 아니면 예외발생 |
| SUPPORTS | Tx이 진행중이건 아니건 상관없이 실행 |
| NOT_SUPPORTED | Tx없이 처리. Tx이 진행 중이면 잠시 중단(suspend) |
| NEVER | Tx없이 처리. Tx이 진행중이면 예외발생 |
>> REQUIRED ==> Default // @Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
- 1개의 트랜잭션으로 처리하며, 오류 발생시 처음으로 Rollback 된다.
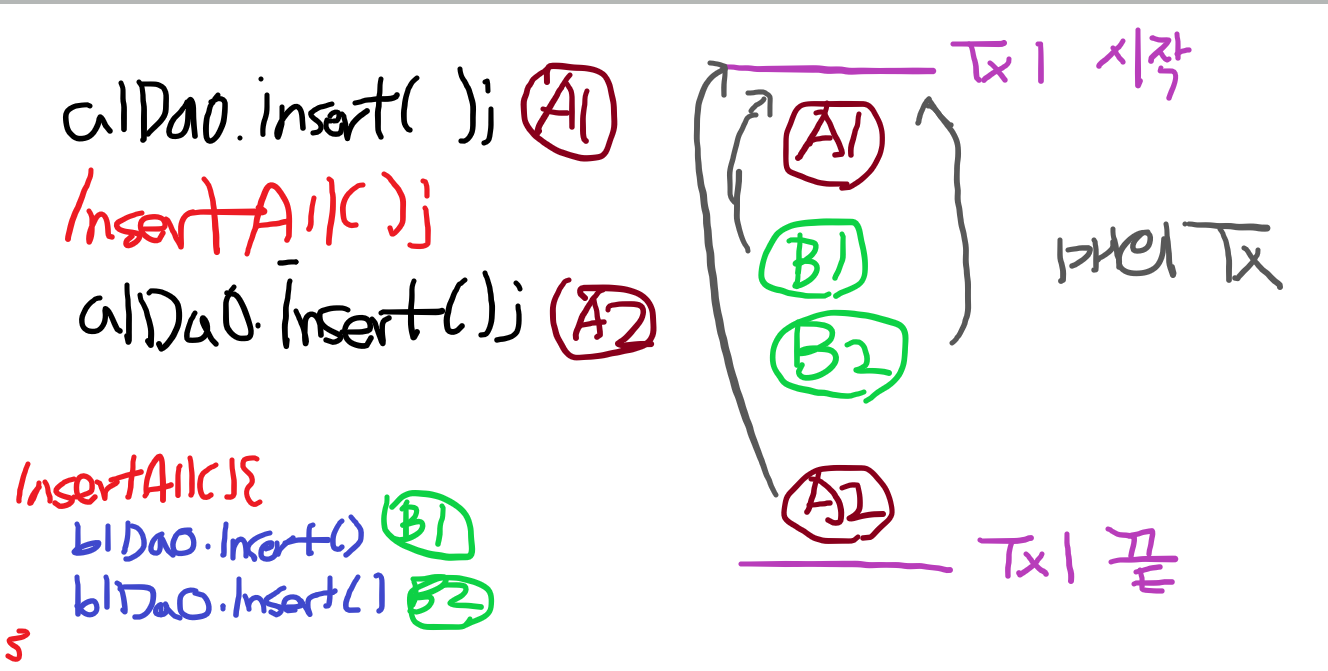
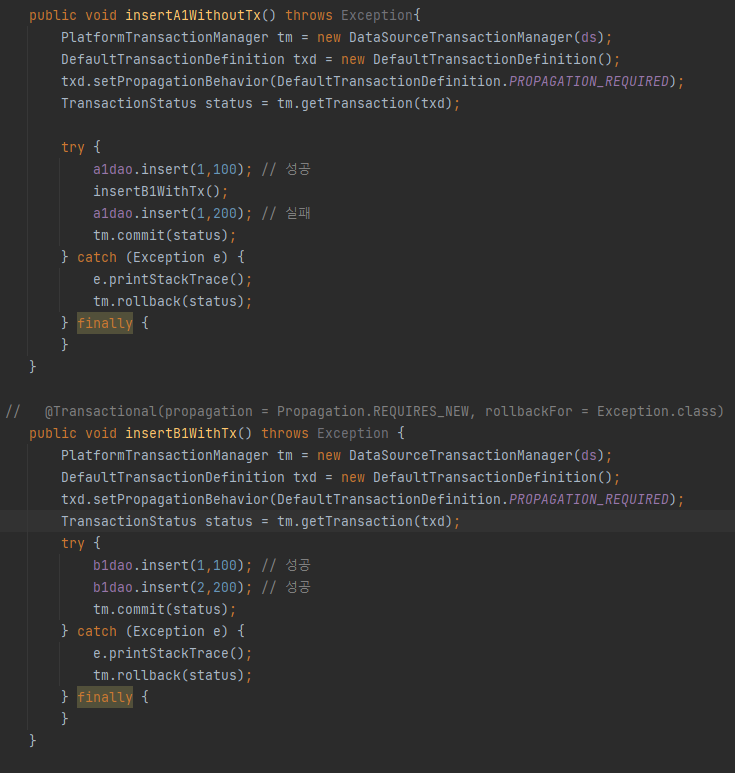
>> REQUIREDS_NEW -- 2개의 Tx 생성된다. // @Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED_NEW)
>> A1, B1,B2 성공했을때 A2가 실패했을경우 A1은 Rollback 되지만
>> B1,B2는 별개의 작업이므로 Rollback 되지 않는다.
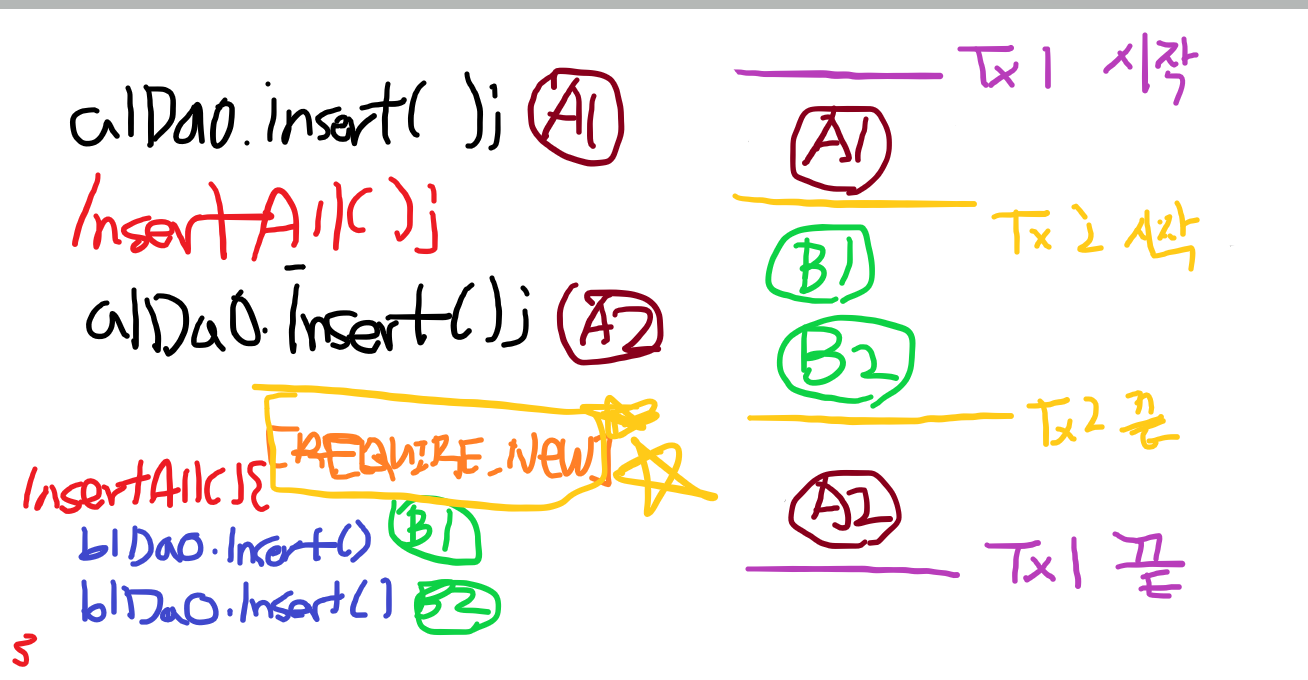
>> REQUIRED 의 경우 ERROR 발생시 처음으로 ROLLBACK된다. 즉 DB에 COMMIT되지 않았다.
>> REQUIRED_NEW
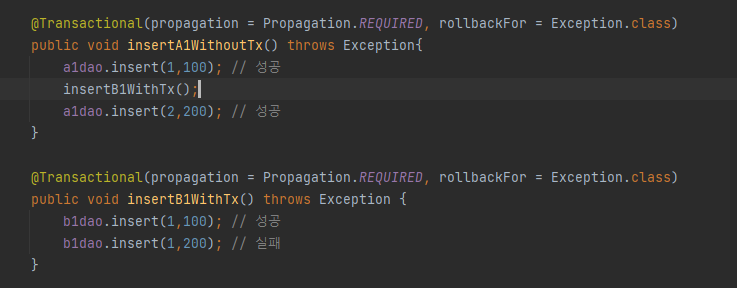
>> insertB1WithTx()의 경우는 다른 Tx이므로 Rollback 되지 않고 commit된다.
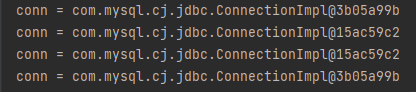
>> @Transactional 어노테이션을 사용하니 같은 클래스 내의 메서드로 해당 REQURED_NEW, REQURED 확인하려고 하니 한개의 conn으로 나온다
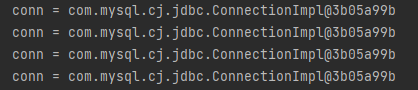

>> 그래서 직접 Tx의 경계를 나눠주고 실행해 봤다.
>> conn이 분리되어 실행되는 것을 확인할 수 있다 (propagaing = REQUIRES_NEW)
>> 즉 insertB1WithTx() 의 실행결과는 다른 Tx로 진행된것이므로 Rollback 되지 않고 commit되었고,
a1dao.insert(1,100), a1dao.insert(1,200)은 Rollback 되어 commit되지 않았다.
========================================================================================
>> @Transactional 의 사용
[1,2] 의경우 primary key 때문에 중복 에러가 발생하게 됩니다.
1. insertA1WithoutTx()
>> insert 실행중 예외 발생시 insert 된것은 commit 되고 나머지는 commit 되지 않음
2. insertA1WithoutFail()
>> (1) @Transactional 어노테이션을 붙였을경우
- RuntimeException , Error만 Rollback 을 해주기 때문에 다른 예외가 발생할 경우 1.과 동일한 결과
>> (2) @Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
- Rollback의 범위를 지정하는것으로, Exception 의 자손 예외까지 모두 Rollback 시켜준다.
3. insertA1WithoutSuccess()
>> 정상적으로 실행된다.
@Service
public class TxService {
@Autowired a1DAO a1dao;
@Autowired B1DAO b1dao;
public void insertA1WithoutTx() throws Exception{
a1dao.insert(1,100);
a1dao.insert(1,200);
}
// @Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class) // Exception을 rollback
@Transactional // RuntimeException, Error 만 rollback
public void insertA1WithoutFail() throws Exception{
a1dao.insert(1,100);
throw new Exception();
//a1dao.insert(1,200);
}
@Transactional
public void insertA1WithoutSuccess() throws Exception{
a1dao.insert(1,100);
a1dao.insert(2,200);
}
}
>> Test 코드
package com.fastcampus.ch3;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations = {"file:src/main/webapp/WEB-INF/spring/root-context.xml"})
public class TxServiceTest {
@Autowired
TxService txService;
@Test
public void insertA1WithoutTx() throws Exception{
txService.insertA1WithoutFail();
// txService.insertA1WithoutSuccess();
// txService.insertA1WithoutTx();
}
}
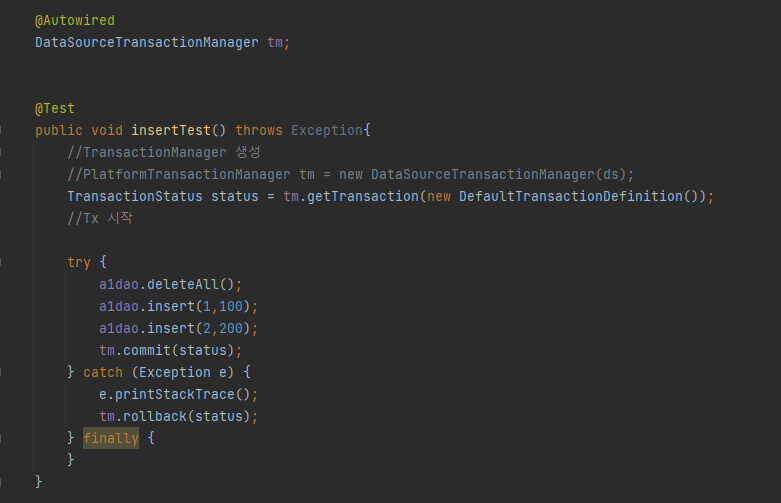
즉 @Transactional 을 사용할 경우 서비스 로직에서 아래와같은 try-catch 문을 자동으로 생성하여 비지니스로직 전, 후로 적용해준다.
'dev > Spring' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Spring] Paging (0) | 2022.07.13 |
|---|---|
| [Spring] Mybatis -1 (2방법) (0) | 2022.07.12 |
| [Spring] @Transactional-1 (0) | 2022.07.12 |
| [Spring] AOP-2 (0) | 2022.07.12 |
| [Spring] Transaction, Commit, Rollback (0) | 2022.07.06 |



